너비 우선 탐색 Depth First Search(DFS)
너비 우선 탐색 Depth First Search(DFS)
이 글은 제 개인적인 공부를 위해 작성한 글입니다.
틀린 내용이 있을 수 있고, 피드백은 환영합니다.
개요
- 너비 우선 탐색(BFS, Breath First Search)은 그래프 탐색 방법 중 하나이다.
- 특정 노드에서 시작해서 인접한 노드를 먼저 탐색하는 방법이다.
- 두 노드 사이의 최단 경로 혹은 임의의 경로를 찾고 싶을 때 BFS를 사용할 수 있다.
- 큐를 이용하여 구현한다.
- BFS는 재귀적으로 동작하지 않는다.
- 장점
- 시작 노드에서 목표 노드까지 최단 길이를 보장한다.
- 단점
- 노드와 연결된 모든 노드들을 큐에 집어넣어 메모리 소모가 크기에, 입력이 큰 경우 DFS를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
- 해가 없다면 유한 그래프의 경우, 모든 그래프를 탐색한 후에 실패로 끝난다. 무한 그래프의 경우에는 해도 못 찾고, 끝내지도 못한다.
과정
- 탐색을 시작할 노드를 방문하고, 큐에 넣은 후 방문했음을 표시한다.
- 큐의 가장 앞에 있는 노드를 꺼낸다.
- 꺼낸 노드의 인접한 노드들 중 아직 방문하지 않는 노드들을 모두 찾아 큐에 넣고 방문했음을 표시한다.
- 큐가 빌 때까지 이 과정을 반복한다.
시간복잡도
- 인접 행렬 : $O(n^2)$
- 인접 리스트 : $O(n+e)$
구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
void bfs(int startNode,
std::vector<std::vector<int>>& adj,
std::vector<bool>& visited)
{
std::queue<int> q;
q.push(startNode);
visited[startNode] = true;
while (!q.empty())
{
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int neighbor : adj[node])
{
if (!visited[neighbor])
{
visited[neighbor] = true;
q.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
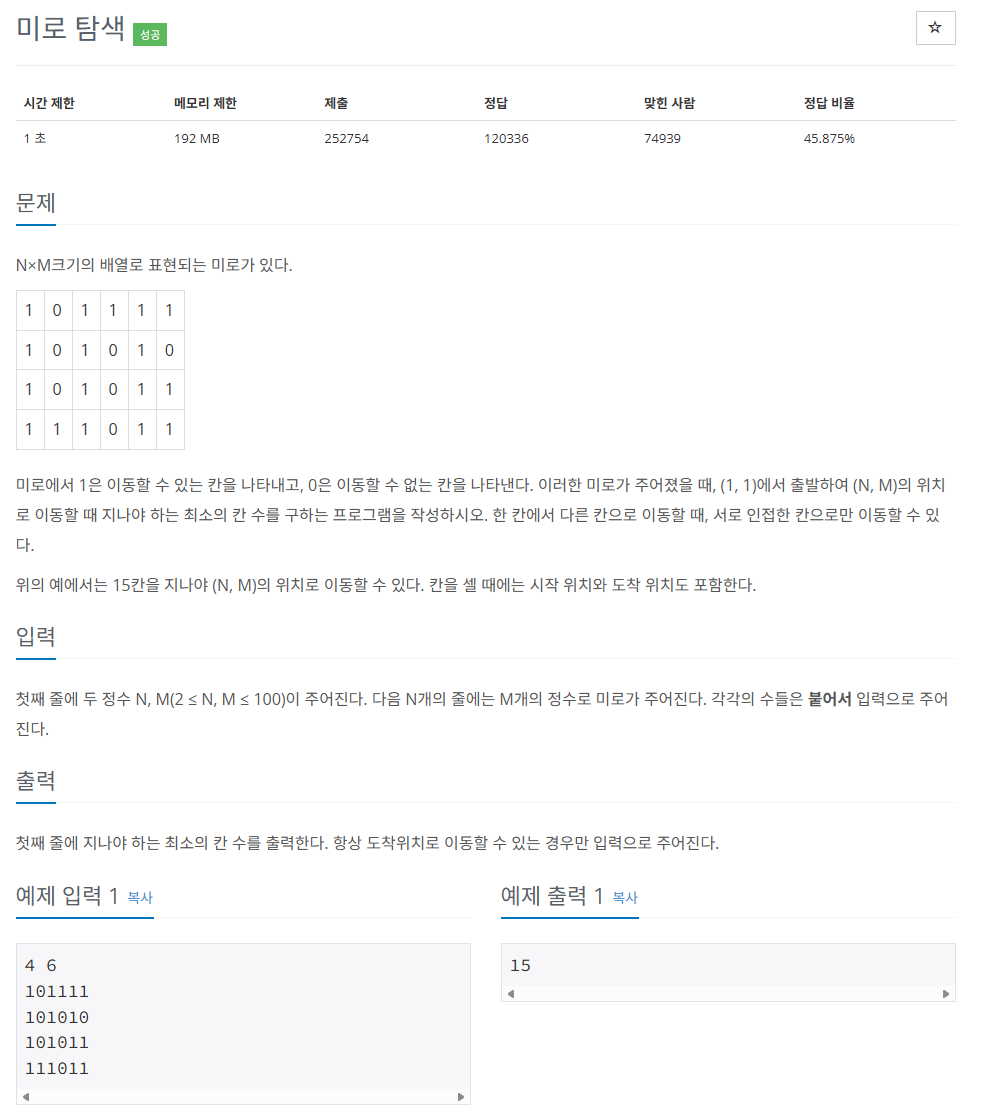
백준 2178번 : 미로 탐색
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
int n, m;
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
void bfs(int i, int j, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& adj, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& cnt)
{
std::queue<std::pair<int, int>> q;
q.emplace(i, j);
while (!q.empty())
{
int x = q.front().second;
int y = q.front().first;
q.pop();
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++)
{
int nx = x + dx[d];
int ny = y + dy[d];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= m || ny < 0 || ny >= n || adj[ny][nx] == 0 || cnt[ny][nx] != 0) continue;
cnt[ny][nx] = cnt[y][x] + 1;
q.emplace(ny, nx);
}
}
}
int main()
{
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr);
std::cout.tie(nullptr);
std::cin >> n >> m;
std::vector graph(n, std::vector<int>(m));
std::vector cnt(n, std::vector(m, 0));
cnt[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
std::string s;
std::cin >> s;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
graph[i][j] = s[j] - '0';
}
}
bfs(0, 0, graph, cnt);
std::cout << cnt[n - 1][m - 1];
return 0;
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.